Actuarial Science
Do you get excited about math, statistics, and finance? Then Dordt’s actuarial science major might be for you. Actuaries help companies manage financial risk through mathematical and statistical modeling. Our program will prepare you to be a thoughtful Christian leader in the field.
Request Info

Program Overview
Dordt's Christ-centered actuarial science program is academically strong. Our faculty have firsthand knowledge of what it takes to be an actuary; they have taken and passed actuarial exams, plus they have worked in the field. Dordt’s actuarial program is taught from a Christian perspective so students can feel equipped to make positive change in the financial industry.

What can I do with an actuarial science degree from Dordt University?
As an actuarial science major at Dordt, you’ll have a chance to pursue a career in the insurance agency as an actuarial analyst, risk analyst, or underwriter. You may also consider a role as an investment analyst or business analyst. Due to the coursework and exam prep you receive as a major, your degree will give you a great head-start on your professional career.
Dordt’s actuarial science program will help you transition from college to workplace by helping you pass your certification exams. Passing at least one (and preferably two) exams before graduating is important, so we emphasize exam preparation starting the fall semester of your first year. Our nationwide network of alumni can help you find an internship, which can typically turn into a job offer before you graduate.
Our graduates work in the insurance and pension management fields, as well as in other financial risk management areas like banks and investment firms, labor unions, and the government. Read more about career prospects and the actuarial science field at www.beanactuary.com.
Research Analyst
A Research Analyst examines and validates the accuracy of data to ensure that it is meaningful information and may reveal business opportunities.
Budget Analyst
Budget Analysts help different organizations plan their finances by preparing budget reports and monitoring their spending.
Financial Adviser
A Financial Adviser is responsible for providing financial guidelines or advice to customers such as investment management, tax planning, and estate planning.
Risk Analyst
A Risk Analyst will advise a company about the potential risks they may face when dealing with new and existing projects.
Career Preparation
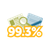
Dordt University's 2024 Career Outcome Rate was 99.3%! “The entire campus is engaged in the work of discipleship,” said Amy Westra, Director of Career Development. “Providing a Christian education focused on Christ-centered renewal is owned by all faculty and staff.”

Actuarial Science Major
The actuarial science major consists of a variety of courses in mathematics, statistics, finance, interest theory, probability, actuarial modeling, communication, and computer programming. The courses required for the major will put you on track to pass at least two actuarial certification exams, if not more, before graduation. That means you’ll be in an excellent position to enter the workforce immediately upon graduation.
Dordt’s Actuarial Science minor is a good option for students who decide later in their college career to pursue actuarial science. It’s also ideal for students who wish to pursue actuarial science along with another major. The minor in actuarial science requires fewer courses but will still put you in a strong position to get a job upon graduation.
To learn more, you can also view the program strengths and learning outcomes for this program.
An actuarial science minor combined with a business-related major can create another path to becoming an actuary. Dordt’s actuarial science minor can help you prepare for actuarial exams as well as internship or entry-level jobs. According to our data, if you have an interest in an actuarial science minor, pursuing it at Dordt is the way to go.
A degree in actuarial science will require students to complete different classes from the business administration, computer science, economics, mathematics, and statistics programs.
- Principles of Financial Accounting: Introduces the concepts and terminology of accounting and financial reporting for modern business enterprises. The course is centered around analyzing and interpreting accounting information for use in making decisions about organizations. There is a special emphasis on analyzing the balance sheet, the statement of income and expense, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity. Additional emphasis is placed on problem-solving, critical thinking, and communication skills that are necessary for forming conclusions about business activities and to communicate these conclusions to others.
- Principles of Managerial Accounting: An introduction to managerial accounting, presenting basic accounting concepts that are important to management decisions. Emphasis is placed on analyzing and interpreting accounting information that enables management accountants to work with managers from other areas, particularly marketing and operations, and to make decisions about costing, pricing, and production. The tools and information that are important are described within the decision framework rather than as isolated accounting procedures.
- Corporate Finance: An introduction to the theory, issues, and practice of business finance. Key components include valuation of financial assets, financial planning and control, working capital management, and capital budgeting.
- Advanced Financial Management: The study of advanced topics in financial management, such as risk analysis, capital structure, dividend policy, mergers, acquisitions, foreign investment, etc. Case analysis will be used extensively.
- Programming I: An introduction to computer programming. Basic notions of abstraction, elementary composition principles, the fundamental data structures, and object-oriented programming technique are introduced. Topics include variables, control structures, arrays, and input/output.
- Principles of Economics: Micro: The study of allocation of scarce resources at the level of the individual, household, and firm. Included are human motivation and preferences, the market, the function of prices, supply, demand, perfect and imperfect competition, and selected policy questions. Christian views on the nature of humanity, human motivation, and the market are also studied.
- Principles of Economics: Macro: An introduction to the study of human choice in the allocation of scarce resources, concentrating on the aggregate or national level. Economic systems, national income accounts and analysis, income distribution, fiscal and monetary policy, banking systems, economic growth, and selected economic policy problems are covered. Christian views on the origin and nature of economic resources and humankind’s stewardship responsibilities are discussed.
- Calculus I: A study of the basic concepts and techniques of calculus for students in all disciplines. Topics include limits, differentiation, integration, and applications. This course is intended for students without any previous calculus credit.
- Calculus II: Continuation of Mathematics 152; a study of transcendental functions, integration techniques, Taylor series approximations, calculus in
polar coordinates, vectors, calculus of vector valued functions and applications of calculus. - Multivariable Calculus: A study of differential and integral calculus of functions of several variables, and line and surface integrals.
- Accelerated Introductory Statistics: This course covers the same content and learning objectives as Statistics 131 but in half the time. This course, along with Statistics 202 and Statistics 203, also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam SRM. Additionally this course, along with Statistics 202, Statistics 203, Statistics 220 and Statistics 352, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS I. Offered first half of spring semester. Credit will not be given for both Statistics 131 and 132.
- Introduction to Financial Mathematics: This course covers topics in basic interest theory including interest, annuities, and amortization as well as basic concepts in derivatives markets including stocks, bonds, forwards, puts, calls, spreads, and hedges. Course content is taught using a guided discovery approach focusing on student conceptual understanding. The course also includes discussion of Christian perspectives on investments and risk management. This course, along with Statistics 218, also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam FM/2. Offered first half of fall semester.
- Econometrics: This course covers all of the topics in Statistics 201 and topics commonly used in economic applications of statistics: time series and forecasting, linear time series models, moving average, autoregressive and ARIMA models, data analysis and forecasting with time series models and forecasting errors. Meets at the same times as Statistics 201 plus two additional hours per week. This course, along with Statistics 132 and Statistics 203, also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam SRM. Additionally this course, along with Statistics 132, Statistics 203, 147, Statistics 220, and Statistics 352, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS I. Offered second half of spring semester. Credit will not be given for both Statistics 201 and 202.
- Generalized Linear Models: This course covers simple linear regression and associated special topics, multiple linear regression, indicator variables, influence diagnostics, assumption analysis, selection of ‘best subset’, nonstandard regression models, logistic regression, and nonlinear regression models. This course, along with Statistics 132 and Statistics 202, also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam SRM. Additionally this course, along with Statistics 132, Statistics 202, Statistics 220 and Statistics 352, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS I.
- Introduction to Univariate Probability: An introduction to the theory and techniques of general probability and common univariate probability distributions. Topics include but are not limited to basic set theory, introductory probability rules (independence, combinatorial, conditionals, Bayes theorem, etc.), common univariate distributions (e.g., binomial and normal) and expected value/variance. This course, along with Statistics 216, also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam P/1. Offered first half of the semester.
- Introduction to Multivariate Probability: An introduction to multivariate probability distributions. Topics include but are not limited to joint probability density functions, conditional and marginal probability distributions, moment generating functions, covariance and correlations, transformations and linear combinations of independent random variables. This course, along with Statistics 215, also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam P/1. Offered second half of the semester.
- Intermediate Financial Mathematics: This course covers intermediate topics in financial mathematics including progressing annuities, force of interest, duration, convexity, immunization, swaps, forwards and other topics on Actuarial Exam FM/2 that are not covered in Statistics 148. This course, along with Statistics 132, also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam FM/2. Offered second half of fall semester.
- Mathematical Statistics: The theory of hypothesis testing and its applications. Power and uniformly most powerful tests. Categorical data and nonparametric methods. Bayesian vs. Frequentist methods. Other selected topics. This course, along with Statistics 132, Statistics 202, Statistics 203 and Statistics 352, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS I. Additionally this course, along with Statistics 290 and Statistics 353, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS II.
- Introduction to Data Science: Introduction to the field of data science and the workflow of a data scientist. Types of data (tabular, textual, sparse, structured, temporal, geospatial), basic data management and manipulation, simple summaries, and visualization. This course also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam PA. Additionally this course, along with Statistics 220 and Statistics 353, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS II.
- Investment and Financial Markets: This course covers the theoretical basis of actuarial models and the application of those models to insurance and other financial risks. This course also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam IFM/3F.
- Long Term Actuarial Mathematics: This course covers the theoretical basis of life contingent actuarial models and the application of those models to insurance and other financial risks. This course also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam LTAM. Additionally this course, along with Statistics 132, Statistics
202, Statistics 203 and Statistics 220, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS. - Short Term Actuarial Models: This course covers product-oriented information relating to short-term insurance (e.g., health, property, and liability) and the basics of pricing and reserving. This course also serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam STAM. Additionally this course, along with Statistics 220 and
Statistics 290, serves as preparation for Actuarial Exam MAS II. - Insurance and Risk Management: Addresses the fundamental issues of risk management, property insurance, liability insurance, life and health insurance, the insurance market, and the operation of insurance companies. Topics to be discussed include the functions of insurance, government regulation, the nature and legal characteristics of insurance documents, marketing, loss adjustment, social insurance programs, employee benefit plans, re-insurance, and the international role of insurance underwriting.
- Advanced Excel: This course focuses on the customization and programmability of Excel spreadsheets. The main topics covered will include writing macros, controlling spreadsheets, databases and other business applications using scripts and short programs.
- Business and Technical Writing: Students will study the process, application, and characteristics of business and technical writing, and the way in which writing style, strategies, content, and clarity will relate practically to one’s profession. Concentrates on developing competence in a variety of writing tasks commonly performed in business, law, industry, social work, engineering, agriculture, and medicine. Satisfies Core Program writing-intensive requirement.
Actuarial Science Minor
For some people, the idea of understanding statistics, mathematics, business, economics, and more in order to help model risk may sound intimidating. But for an actuarial science minor, it’s invigorating. If you love figuring out how to apply math and statistical models to real situations, consider an actuarial science minor from Dordt.
Learn More

Ready to take the next step?
Faculty
With experience in a variety of fields, our faculty members are equipped and ready to help you succeed.
Faculty Info
Student Stories
Dordt students and alumni use their gifts to make a difference in the world. Check out their stories to see how Defender Nation lives out our mission to work effectively toward Christ-centered renewal in all aspects of contemporary life.

Connect with us
Submit your information to request more information about Dordt and this program. We'll also use this information to connect you with your admissions counselor!
Related Programs
Still looking for the right fit? Here are some additional program options that we think might interest you or are often paired with this program. You can also view the programs page to keep exploring your options.











