Architecture
This degree focuses on the engineering science that goes into creating and designing a beautiful, energy-efficient building. Along with that, it also includes building structures that can withstand disaster.
Request Info

Program Overview
This degree will help you to use your creativity and logic to innovate. We focus on a degree that focuses on sustainable, efficient, and environment-proof design.
What You'll Learn
By choosing an emphasis in architecture within the engineering science major, you'll take courses in art, engineering, and construction management. This is on top of courses that you'll take for the engineering science major, including courses in chemistry, mathematics, physics, and statistics.
What You Can Do With An Architecture Emphasis
With an architecture emphasis for the engineering science major, you'll gain a strong understanding of architecture best practices and how they align within the field of engineering. You'll learn about structural theory, design, safety imperatives, and more.
Architectural Project Manager
Architectural Project Managers are responsible for overseeing and managing the many different aspects of an architectural project.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer performs tasks that deal with the design and specifications of a construction site.
Mechanical Designer
A Mechanical Designer creates the design drafts of different mechanical devices and products.
Career Preparation
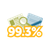
Dordt University's 2024 Career Outcome Rate was 99.3%! “The entire campus is engaged in the work of discipleship,” said Amy Westra, Director of Career Development. “Providing a Christian education focused on Christ-centered renewal is owned by all faculty and staff.”

Students looking to study architecture engineering will take classes from a variety of programs including art, engineering, environmental studies, and construction management in addition to completing the general requirements for an engineering science degree.
- Design Theory: Manipulation of two-dimensional design through the use of the basic art elements: line, shape, value, color, texture, and space. The course is intended to develop a visual vocabulary and an imaginative approach to design.
- Drawing I: Acquiring the basic skills of drawing through an objective investigation of reality. Common media and tools are used.
- Graphic Design I: An introductory class in the use of the Macintosh computer, covering basic layout software, object-oriented drawing software, and a paint program for scanning, image manipulation, and their use in graphic design. Through assignments that address the functional and experimental aspects of typography, students explore the interaction of form and meaning in typographic design. This course provides an initial exploration of visual communication issues and applications along with design methodology.
- Art History: Ancient and Medieval: This course is the first of a three-semester survey of the history of the visual arts. It investigates the role of the visual arts in the historical and cultural development of world civilization between prehistory and the 14th century.
- Art History: 14th to 19th Centuries: This course is the second of a three-semester survey of the history of art. It covers the history of architecture, painting, and sculpture from the 14th century through the 19th century.
- Art History: Contemporary Art and Architecture: This is the third course in a historical survey of art and architecture. The course will begin with the foundations of modernism in the last half of the 19th century and then cover the plurality of styles in the 20th century.
- Non-Western Art History: This course studies non-European art and culture including Islamic, Japanese, and Chinese art.
- Statics: A mechanics course that examines the effects of forces and moments applied to rigid and deformable bodies in equilibrium. Students will analyze concentrated and distributed force systems applied to static particles, rigid bodies, trusses, frames, and machines.
- Mechanics of Materials: A solid mechanics course that examines the stresses, strains, and deformations that develop when various loads (tension, compression, torsion, bending, or any combination of these loads) are applied to deformable bodies. Elements of structural design are introduced using safety factors and failure criteria for ductile materials. The mechanics design laboratory provides an introduction to experimental methods, hands-on experience applying and using strain gages and investigating beam loading, and an introduction to finite-element analysis (FEA) software.
- Introduction to Thermal-Fluids: An introduction to the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer principles, including energy, work, heat, properties of pure substances, the first and second laws, and other thermal-fluid relations.
- History of Science and Technology: Enables the student to examine from a Reformed, biblical perspective the narrative of scientific unfolding and technological development as two human activities that are manifest in all cultures. Emphasis is on the major paradigms and events that have shaped the development of science and technology in the West and most recently in North America. The course focuses on the historical activity of engineers and artisans, while investigating the interrelationship between scientific thought and technological development. Events and ideas such as the philosophical origins of Western science, the Copernican revolution, Enlightenment rationalism, the industrial revolutions, 20th century positivism, the Einsteinian revolution, and the modern systemization ethic are discussed.
- Introduction to Environmental Studies I: An introduction to contemporary environmental studies and creation care, with emphasis on class discussion of relationships between human population and resource use in light of biblical teaching about environmental stewardship. Particular attention is given to the biotic and ecological dimensions of creation stewardship and planetary distress. Designed to be taken by environmental studies majors concurrently with Environmental Studies 161.
- Introductory Geology and Physical Geography: A general introduction to the physical nature and structure of the solid Earth, including, briefly, its physical geography and a more detailed look at its geology. The environmental implications of these subjects are detailed. Three lectures and one laboratory period of three hours per week plus one overnight field trip and one or two shorter trips.
- Meteorology and Climate Change: Provides a general introduction to meteorology and weather. Climate and climate change in Quaternary times to the present are also considered. The implications of an anthropogenically enhanced greenhouse effect will be addressed, with particular attention given to the impact of these changes on the structure and function of ecosystems. Includes one or two field trips to relevant sites in the region.
- Principles of Construction Management: An introductory survey course in construction management that begins by building a Christian perspective on the task and calling of a construction manager or construction engineer. The course introduces methods of construction project planning, scheduling, delivery, quality, and control. It also introduces construction contract types, construction cost estimating and accounting, along with an overview of construction method, practice, and safety.
- Construction Communication and Architectural Graphics: This lab studio course introduces architectural and construction communication by practicing methods of construction documentation and preparation. The course will introduce students to basic plan reading. Construction planning computer applications and architectural computer-aided drafting will be explored and practiced.
- Geographic Information Systems and Surveying: Even An introduction to the acquisition, analysis, display, manipulation, and management of geographic information. Course topics will include geographical data input, storage, maintenance, analysis, and retrieval. Students will utilize common GIS software and associated hardware. An overview of survey methods used to gather and quantify features of physical geography will be included. The course will meet in two studio lab classes to provide an integral learn-by-doing experience applying GPS technology, survey methods, and GIS applications. Application of GIS to agriculture, business, environmental management, and other disciplines will be provided in this course.
- Construction Materials and Methods: A comprehensive study of the properties, sources, processing, methods, sequences, and equipment used in residential and commercial construction projects. Planning and managing of the construction process, including an introduction to structural and finish systems that make up building structures, are investigated. Appropriate application and responsible use of materials for design and functional intent is investigated. The environmental impact of construction is discussed.
- Mechanical and Electrical Systems: A study of the construction of mechanical and electrical systems, emphasizing principles of heating, cooling, ventilation, water supply, waste disposal, and electrical distribution. An introduction to mechanical, electrical, and plumbing codes and design software included. Energy conservation issues, sustainable design principles, and use of renewable energy are addressed.
- Project Management: This course is an introduction to the field of project management. The primary objective is to acquaint students with a broad basic overview of project management and the role of a project manager throughout the five primary processes of managing projects. The course will also cover common agile methodologies and principles because of how they relate to project management. The agile project management process encourages frequent inspection and adaptation, teamwork, accountability, self-organization, best practices that allows for rapid delivery and high quality, and a business approach that aligns development with customer needs and company goals. Prerequisite: sophomore standing.
- Construction Estimating: An introduction to construction estimating and bid preparation with an emphasis on quantity takeoff. Includes a detailed study and application of pricing, subcontract evaluation, and bidding techniques using blueprints and specifications. Project types studied include residential, light commercial, and commercial building projects.
- Elements of Materials Science: Studies the relationship between structure and properties of various materials, including metals, ceramics, polymers, and semiconductors. Students will learn how atomic and molecular arrangements, as well as manufacturing processes, influence the mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties of a material. Introductory topics in metallurgy in this course include the examination of effects of processing (heat treatment and manufacturing) and service environment on microstructure and properties. Laboratory explorations in materials engineering introduce concepts in experimental design and data analysis.
- Fluid Mechanics: comprehensive, introductory course in fluid mechanics covering: hydrostatics; control volume approach to the continuity, momentum, and energy equations; dimensional analysis, similitude, and modeling; introductory boundary layer theory; fluid drag and lift; flow through conduits, pumps and compressors; and hydraulics and open channel flow. All students participate in team design projects involving design of water supply, irrigation, air handling system, or other complex fluid dynamics system.
- Heat Transfer: Studies of the three modes of heat transfer (conduction, convection, and radiation) with application to heat exchangers. Computer methods are used extensively for heat transfer design and analysis. A formal heat exchanger design project is included in this course.
- Structural Analysis: A study of the analysis of trusses, beams, and framed structures. Students will learn how to determine loads on structures, including dead loads, live loads, and environmental loads. Shear, moment, and deflected shape diagrams will be considered. Deformation calculations, approximate analysis methods, flexibility methods, and stiffness methods for the analysis of indeterminate beams and frames will be considered. Influence lines for determinate and indeterminate beams will be introduced.
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation Design: A study of the engineering principles relating to soil properties and foundation design. The material properties of soil including structure, index properties, permeability, compressibility, and consolidation will be explored. Methods of soil testing, identification, and remediation will be covered. Principles of settlement and stresses in soils will be considered. Slope stability, retaining walls, and bearing capacity of shallow foundations will be introduced. The soils lab will provide hands-on opportunities to determine water content, perform sieve analyses, and test liquid, plastic, and shrinkage limits. Soil classification, compaction, compression, and consolidation testing will be explored.
- Environmental Engineering: An introduction to water supply and wastewater treatment, solid waste management, hazardous waste disposal, pollution control equipment, and other topics relating to the engineer’s role for ensuring clean air and providing clean water to communities. Methods and equipment for monitoring and testing air and water quality will be examined.
- Sustainable Energy Systems Design: A senior-level design course that focuses on designing energy systems for conservation, sustainability, and efficiency. Methods of auditing energy utilization and design principles for energy conservation are addressed as are solar and renewable energy technologies for meeting residential, commercial, and industrial energy needs. A variety of computer tools will be used for system analysis. A design studio component may incorporate tours, community service projects, and design projects relating to energy utilization and conservation.
- Reinforced Concrete Design: Analysis and design of reinforced concrete beams, columns, one-way slabs, and frames. The design of members for axial load, flexure, shear, deflections, bond, and anchorage will be considered. Design will be based primarily on ACI strength design methods.
- Structural Steel Design: A study of design and behavior of steel members and structures. The design of steel beams, columns, tension members, frames, trusses, and simple connections will be considered. Design will be based primarily on AISC specifications related to the load and resistance factor design method. Allowable stress design will be introduced.
Ready to take the next step?
Faculty
With experience in a variety of fields, our faculty members are equipped and ready to help you succeed.
Science and Technology Center
While studying engineering science, you'll have the opportunity to spend time in Dordt's Science and Technology Center. Informally known as the "Science Building," the Science and Technology Center is home to labs for mechanical engineering, electronics, electrical engineering, and computer-aided design.
Learn more


Student Stories
Dordt students and alumni use their gifts to make a difference in the world. Check out their stories to see how Defender Nation lives out our mission to work effectively toward Christ-centered renewal in all aspects of contemporary life.

Connect with us
Submit your information to request more information about Dordt and this program. We'll also use this information to connect you with your admissions counselor!
Related Programs & Emphases
Still looking for the right fit? Here are some additional program options that we think might interest you or are often paired with this program. You can also view the programs page to keep exploring your options.







